Breast Cancer
Like other cancers, breast cancer is an uncontrolled growth of breast cells. Breast cancer occurs as a result of abnormal changes or mutation in the genes responsible for regulating the healthy growth of breast. The genes are in each cell’s nucleus, which acts as the “controller” of concern cell.
Mutation in gene disturb/mislead the normal process of the cell, because of that cells starts abnormaly and uncontrolled growth, producing more cells just like it and forming a tumor like structure.
This abnormal tumour-like growth can be benign (not cancerous) or malignant (cancerous property). Benign tumours are close to normal in appearance, they grow comparatively slowly, and they do not invade or spread to nearby tissue and other parts of the body. As malignant cells have the potential to grow as cancer If they left unchecked or untreated, they eventually can spread to nearby tissue and beyond an original tumour to other parts of the body.
Types of Breast cancer include:
- Angiosarcoma
- Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
- Inflammatory breast cancer
- Invasive lobular carcinoma
- Male breast cancer
- Paget's disease of the breast
- Recurrent breast cancer
Most common signs and symptoms include:
- A breast lump or thickening that feels different from the surrounding tissue
- Change in the size, shape or appearance of a breast
- Changes to the skin over the breast, such as dimpling
- A newly inverted nipple
- Peeling, scaling, crusting or flaking of the pigmented area of skin surrounding the nipple (areola) or breast skin
- Redness or pitting of the skin over your breast, like the skin of an orange
Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy, quadrantectomy)
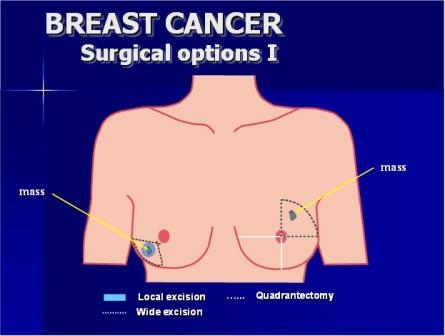
Breast-conserving surgery is an advanced form of lumpectomy or wide local excision, where just the tumour and a little surrounding breast tissue is excised. Breast-conserving surgery also known as a quadrantectomy or partial mastectomy.
In breast-conserving surgery, the part of breast tissue excised will depend on:
- The size of a tumour and where it is in your breast
- The size of your breasts
- The type of cancer you have
- The area of surrounding tissue that needs to be removed.
The surgeon will always remove healthy surrounding breast tissue around the cancer part, which will be taken for biopsy to detect the extension of cancer.
If there's no cancerous tissue present in the surrounding healthy tissue, there's less chance that cancer will reoccur.
If cancer cells are seen in the surrounding tissue, more tissue may need to be removed from the affected part.
After having breast-conserving surgery, you'll usually be offered radiotherapy to destroy any remaining cancer cells. breast
Top Doctors In India For Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy, quadrantectomy)

Dr. Amit Agrawal
26 years of experience , New Delhi, Delhi/NCR, India

Dr. Sushant Mittal
10 years of experience , New Delhi, Delhi/NCR, India

Dr. Samit Purohit
10 years of experience , New Delhi, Delhi/NCR, India

Dr. Chandragouda Dodagoudar
18 years of experience , New Delhi, Delhi/NCR, India
Top Hospitals In India For Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy, quadrantectomy)
Jaypee Hospital, Noida
Established in : 2013
BLK Super speciality hospital, New Delhi
Established in : 1959
Artemis Hospital, Gurugram
Established in : 2007
Max Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
Established in : 2006






